In the realm of prostate cancer diagnosis and management, multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) and digital histopathology stand as pivotal technologies. Each brings unique capabilities to the table, yet their comparison reveals a complex interplay of strengths and limitations that could shape future diagnostic pathways and treatment strategies.
Capabilities and Limitations:
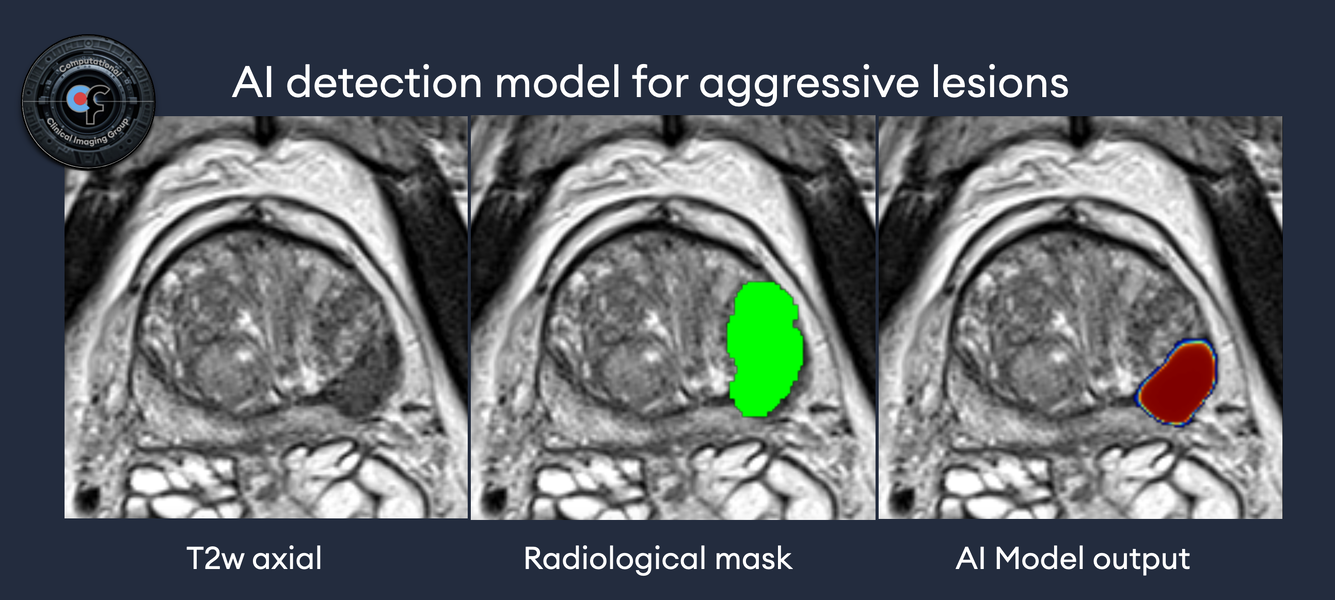
mpMRI has revolutionized prostate cancer detection, offering a non-invasive method to visualize tumor characteristics and guide biopsy decisions. Its high sensitivity in identifying clinically significant prostate cancer is a testament to its value in the diagnostic workflow. However, the technology is not without its limitations. Studies have shown that mpMRI may underestimate tumor volume, particularly in lesions with intermediate density or heterogeneous morphology. This underestimation could have significant implications for active surveillance and focal treatment strategies, potentially impacting patient outcomes.
Digital histopathology, on the other hand, provides a microscopic view of the disease, allowing for detailed analysis of tumor subpatterns and architecture. While it offers unparalleled precision in diagnosing and grading cancer, its reliance on invasive biopsy or prostatectomy samples limits its applicability in ongoing patient monitoring.
Opportunities for AI Models:
The integration of AI models with mpMRI data presents an exciting frontier. AI has the potential to enhance mpMRI’s diagnostic accuracy, enabling more precise tumor volume estimation and detection of lesions that are currently underrepresented. By learning from vast datasets, AI algorithms could identify subtle imaging patterns linked to specific histopathological features, bridging the gap between non-invasive imaging and microscopic disease characterization.
Challenges in Using mpMRI as Ground Truth for AI Training:
Relying on mpMRI as the ground truth for training AI models introduces challenges. The variability in tumor visibility on mpMRI, influenced by factors such as tumor density and morphology, could lead to biased algorithms that miss certain cancer subtypes. Furthermore, the lack of consensus on prostate cancer delineation in mpMRI complicates the standardization of training datasets, potentially limiting the generalizability of AI models.
Conclusion:
The comparison between mpMRI and digital histopathology underscores the complementary nature of these technologies in prostate cancer management. While each has its limitations, their integration, especially through AI, offers a promising path forward. However, careful consideration must be given to the challenges of using mpMRI as a training ground for AI models. As we navigate these complexities, the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes remains immense. Let’s continue the conversation and explore these opportunities together. Share your thoughts and experiences to further our collective understanding in this vital area of cancer care.